Experts estimate that cybercrime might end up costing businesses a staggering $6 trillion. Organizations are focusing on how to strengthen cybersecurity in any sector, and the concern is understandable. After all, cyber attacks, including intellectual property, can dramatically affect efficiency, credibility, and company property.
A cybersecurity audit is a comprehensive review of your organization’s information systems to ensure they are operating smoothly and efficiently. It can also save your organization money. For example, you may discover enforcement problems that can lead to fines and potentially impact customer retention.
Security audits ultimately help ensure that the business is secure and that confidential information is appropriately maintained and managed. We’ll cover four types of security audits in this blog that you should regularly conduct to protect your business, employees, and customers.
In the world of cybersecurity, ensuring the safety and protection of sensitive data is paramount. This is where security audits come into play. Security audits are comprehensive examinations of an organization’s systems and processes, conducted to identify potential vulnerabilities and assess overall security measures. By conducting these audits, businesses can gain a better understanding of their security infrastructure and make informed decisions to safeguard against potential threats. This article will explore the different types of security audits and delve into what exactly constitutes a security audit.
Definition of Security Audits
Explanation of Security Audits
security audits are systematic and thorough evaluations of an organization’s security measures and controls. These audits are designed to identify vulnerabilities, assess risks, and evaluate the effectiveness of existing security protocols. By conducting security audits, organizations can gain valuable insights into their security posture and make informed decisions to enhance their overall security.
A security audit (check) is a systematic review of the safety of the information system of an organization by measuring how well it meets a set of criteria. The security of the physical configuration and environment, software, information management processes, and user practices is usually evaluated by a complete examination to avoid risks
Safety audits often used to determine the application of rules, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, Sarbanes-Oxley Law, and the Law on the Breaches of California Security that prescribe the treatment of information by enterprises.
Purpose of Security Audits
The primary purpose of security audits is to safeguard an organization’s assets, systems, and sensitive information. By examining security processes and controls, security audits aim to identify weaknesses and potential gaps in security measures. These audits also help in assessing compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices. Furthermore, security audits serve as a proactive measure to mitigate risks, prevent security breaches, and protect against emerging threats.
Importance of Security Audits in Today’s Digital Era
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, security audits play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of information. With the growing adoption of technological advancements, organizations face numerous security challenges that can lead to severe damages, both financially and reputationally. Security audits help in mitigating these risks by identifying vulnerabilities, improving security protocols, and enhancing overall organizational resilience.
When you keep track of even a little bit of cybersecurity news, you should have an intuitive understanding of why audits are essential. Daily audits can identify new vulnerabilities and unintended effects of organizational change, and specific sectors, mainly medical and financial ones, are mandated by law.
Processes Involved in Security Audits
Identification of Assets and Systems
The first step in conducting a security audit is to identify the key assets and systems within an organization. This includes identifying critical infrastructure, sensitive data repositories, network devices, software applications, and physical resources. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s assets and systems, auditors can prioritize their evaluation efforts and focus on areas that require heightened attention.
Developing an Audit Strategy
Once the assets and systems have been identified, auditors develop an audit strategy tailored to the specific organization’s needs. This includes determining the scope of the audit, defining objectives, establishing evaluation criteria, and selecting appropriate audit methodologies. The audit strategy serves as a roadmap for conducting a thorough assessment and ensures that the audit aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Execution of the Audit
The execution phase involves conducting the actual security audit based on the predefined strategy. Auditors employ a variety of techniques, such as vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, code review, and security log analysis. During this phase, auditors systematically evaluate the effectiveness of controls, identify vulnerabilities, and assess the organization’s adherence to policies, standards, and regulations. This process often involves collaboration with relevant stakeholders and subject matter experts within the organization.

Reporting Audit Findings
After collecting and analyzing the necessary data, auditors compile their findings into a comprehensive audit report. The report typically includes detailed descriptions of vulnerabilities, identified risks, areas of improvement, and recommendations to enhance security measures. Clear and concise reporting is crucial to ensure that the organization understands the significance of the audit findings and can take appropriate action to address the identified issues.
Reviewing and Revising the Audit Process
The final step in the security audit process involves reviewing and revising the overall audit methodology and processes. This continuous improvement approach ensures that the audit remains up-to-date with the ever-evolving threat landscape and incorporates emerging best practices. By assessing the effectiveness of the audit process, organizations can enhance their security measures, better prioritize resources, and strengthen their overall security posture.
Types of Security Audits
Internal Security Audits
Internal security audits are conducted by personnel within the organization itself, often from the internal audit department or dedicated security teams. These audits focus on evaluating internal controls, policies, and procedures. Internal security audits provide organizations with an independent assessment of their security measures and an opportunity for proactive risk mitigation.
External Security Audits
External security audits are performed by independent third-party auditors or consulting firms. These audits provide an objective evaluation of an organization’s security controls, policies, and practices. External security audits are often required by regulatory bodies, industry standards, or contractual obligations. They offer an unbiased assessment that can uncover potential blind spots and identify weaknesses that internal audits may overlook.
IT Security Audits
IT security audits focus specifically on an organization’s information technology infrastructure and systems. These audits examine aspects such as network security, data protection, access controls, incident response capabilities, and disaster recovery plans. IT security audits ensure the implementation of effective IT security measures to mitigate risks associated with cyber threats.
Physical Security Audits
Physical security audits assess an organization’s physical assets, facilities, and infrastructure. These audits examine areas such as access controls, surveillance systems, alarm systems, and security personnel protocols. Physical security audits help identify vulnerabilities in perimeter defense, visitor management, and surveillance systems, ensuring that appropriate measures are in place to protect physical assets.

Compliance Security Audits
Compliance security audits focus on assessing an organization’s adherence to relevant laws, regulations, and industry-specific requirements. Auditors evaluate various compliance frameworks and standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Compliance security audits help organizations ensure that they meet legal obligations and avoid penalties or legal repercussions.
Roles and Responsibilities in Security Audits
Role of Auditors
Auditors in security audits are responsible for conducting independent evaluations and assessing an organization’s security controls and practices. Their role is to identify vulnerabilities, evaluate risks, and make recommendations for improvement. Auditors bring expertise in information security and employ a variety of tools, techniques, and frameworks to ensure a comprehensive assessment.
Responsibilities of the Organization Being Audited
The organization being audited has a vital role in facilitating the security audit process. Responsibilities include providing auditors with access to necessary resources, such as documentation, systems, and personnel. The organization needs to collaborate with auditors, provide accurate information, and address any concerns or questions raised during the audit. It is crucial for the organization to take auditors’ recommendations seriously and prioritize the implementation of necessary security measures.
Interaction between Auditors and the Organization
Effective communication and collaboration between auditors and the organization being audited are essential for a successful security audit. Regular meetings, interviews, and data collection sessions allow auditors to gain a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s security measures. Organizations should also provide auditors with relevant documentation, policies, and access to systems to facilitate the audit process. Through open dialogue and mutual cooperation, auditors and the organization can work towards achieving the common goal of enhancing security.
Tools and Techniques Used in Security Audits
Use of Automated Tools for Audits
Automated tools play a significant role in security audits as they enable auditors to conduct more comprehensive and efficient assessments. Vulnerability scanners, network analysis tools, and log analysis tools are examples of automated tools used to identify vulnerabilities, detect malicious activities, and analyze logs. These tools help auditors gather large amounts of data, perform in-depth analysis, and identify potential security risks.
Manual Techniques
In addition to automated tools, auditors also employ manual techniques to ensure a thorough evaluation. Manual techniques involve reviewing policies and procedures, examining physical security controls, and conducting interviews with relevant personnel. Manual techniques allow auditors to gain a deeper understanding of an organization’s security posture and identify any gaps that may go unnoticed by automated tools.

Hybrid Approaches
Many security audits utilize a combination of automated tools and manual techniques to create a hybrid approach. This approach leverages the strengths of both methods, allowing auditors to conduct comprehensive assessments while minimizing false positives and false negatives. By combining automated tools for data collection and analysis with manual verification and validation, auditors can ensure a more accurate assessment of an organization’s security measures.
Role of AI and Machine Learning in Security Audits
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies are increasingly being integrated into security audits. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and identify anomalies that may indicate security risks. AI and ML can automate certain aspects of the audit process, such as log analysis and anomaly detection, allowing auditors to focus on more complex tasks and make more informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
Best Practices in Security Audits
Preparation for the Audit
Proper preparation is crucial for a successful security audit. Organizations should ensure that they have sufficient documentation, policies, and procedures in place before the audit begins. This includes regularly updating and maintaining an inventory of assets and systems, documenting security controls, and implementing appropriate security measures. By preparing adequately, organizations can streamline the audit process and ensure a more comprehensive evaluation.
Involvement of Stakeholders
Engaging stakeholders throughout the audit process is essential for effective security audits. Stakeholders include individuals from various departments, such as IT, legal, compliance, and senior management. Involving stakeholders ensures that all relevant perspectives are considered, facilitates a better understanding of potential risks, and increases the chances of successful implementation of audit recommendations. Regular communication and collaboration with stakeholders foster accountability and support for security efforts.
Accurate Reporting
Clear and accurate reporting is vital for conveying the significance of audit findings and recommendations to the organization. Audit reports should provide a detailed analysis of weaknesses, risks, and potential impacts on the organization’s security posture. The reports should also include practical recommendations for improvement, prioritized based on risk severity. By providing accurate and actionable information, organizations can make informed decisions to enhance their security measures.
Follow-up after the Audit
After the audit is completed, organizations should prioritize the implementation of necessary changes and improvements based on the audit findings and recommendations. This involves developing a plan of action, assigning responsibilities, and establishing timelines for remediation. Regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial to ensure that the recommendations are effectively implemented, and the organization’s security posture is continuously improved.
Benefits of Security Audits
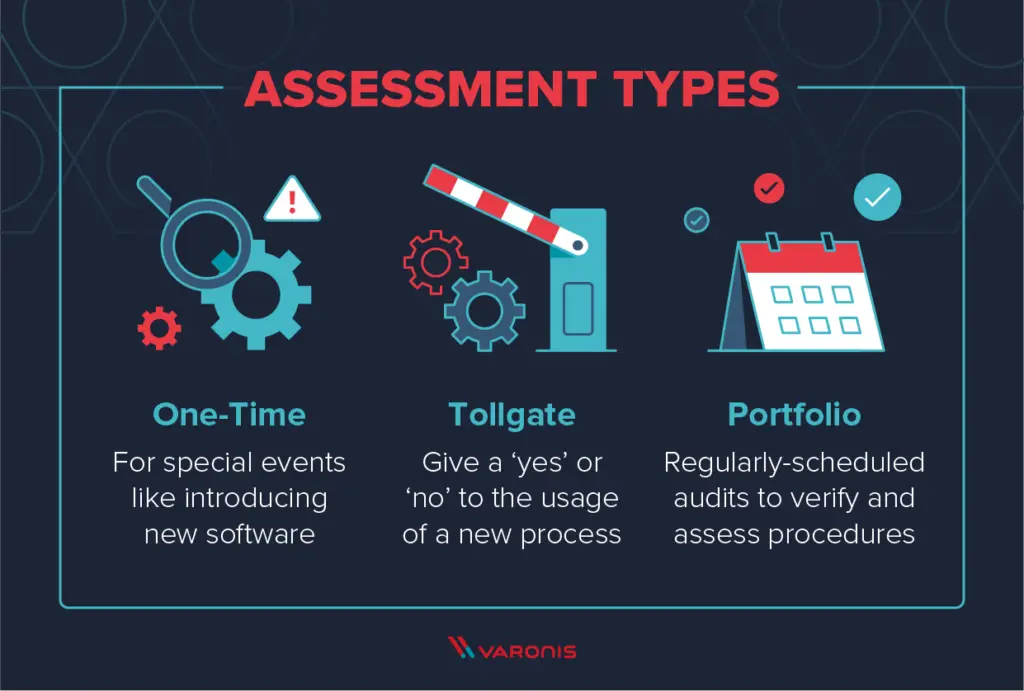
Identifying Security Risks
One of the primary benefits of security audits is the identification of security risks. Audits help organizations proactively uncover vulnerabilities, assess their potential impact, and mitigate risks before they can be exploited by malicious actors. By identifying security risks, organizations can prioritize resources and implement appropriate security measures to protect against potential threats.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with regulations and industry standards is crucial for organizations, especially those operating in highly regulated sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government. Security audits help ensure that an organization’s security measures align with legal requirements and industry regulations. By demonstrating compliance, organizations can avoid penalties, maintain customer trust, and protect their reputation.
Improving Organization’s Security Posture
Security audits provide organizations with insights into their current security posture and areas for improvement. By implementing the recommendations made through these audits, organizations can enhance their overall security measures and reduce the likelihood of security breaches. Improving an organization’s security posture not only safeguards critical assets but also strengthens the organization’s resilience against emerging threats.
Increasing Customer Confidence
In today’s digital era, customers place significant importance on the security practices of organizations they engage with. By conducting security audits, organizations can demonstrate a commitment to ensuring the security of customer data and protecting their privacy. High levels of security assurance can help build customer trust, enhance brand reputation, and differentiate organizations from competitors in the market.
Challenges in Conducting Security Audits
Dealing with Complex Systems
Organizations often operate in complex technological environments with interconnected systems, networks, and applications. Assessing the security of these complex environments presents numerous challenges for auditors. Auditors need to have a deep understanding of various technologies and architectures to effectively evaluate the security controls and identify potential vulnerabilities. Complex systems require auditors to adapt their methodologies and techniques to ensure a comprehensive assessment.
Overcoming Resistance from within the Organization
Some organizations may resist the idea of security audits due to concerns about exposing vulnerabilities or the potential disruption to business operations. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication and a proactive approach to educate stakeholders about the importance and benefits of security audits. Organizations need to foster a culture of security awareness and emphasize the value of audits as a proactive measure to protect against potential threats.
Maintaining Objectivity
Maintaining objectivity can be a challenge, especially when internal auditors are conducting the security audit. Internal auditors may face biases or conflicts of interest that could hinder their ability to provide an unbiased assessment. To address this challenge, organizations may opt for external auditors who bring a fresh perspective and can provide an independent evaluation of security measures.
Keeping up with Changing Technology and Threats
The ever-evolving nature of technology and emerging threats pose challenges for security audits. Auditors must continuously update their knowledge and skills to keep pace with the latest developments in the cybersecurity landscape. It is crucial for auditors to stay informed about emerging threats, new attack vectors, and evolving regulatory requirements. Adapting audit methodologies and techniques to address constantly changing technology and threats is essential to ensure the effectiveness of security audits.
Future Trends in Security Audits
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, introduce new security challenges for organizations. Security audits need to evolve and adapt to assess the security controls and risks associated with these technologies. Auditors will need to gain expertise in evaluating the security of IoT devices, cloud infrastructure, and AI-driven systems to ensure a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s security posture.
Threat Landscape Evolution
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new attack vectors, sophisticated techniques, and emerging threats. Security audits must stay vigilant to address these evolving threats effectively. Auditors need to anticipate emerging risks, develop new methodologies, and leverage advanced tools and techniques to assess an organization’s ability to detect, prevent, and respond to these threats. Continuous monitoring and regular updates to audit processes are crucial to maintaining the relevance and effectiveness of security audits.
Changes in Regulatory Environment
Regulatory requirements surrounding cybersecurity are constantly evolving to keep pace with emerging threats. Security audits will need to adapt to changes in the regulatory environment to ensure compliance and provide an accurate assessment of an organization’s security measures. Auditors must stay updated on new regulations, compliance frameworks, and industry-specific standards to incorporate them into the audit process effectively.
Case Studies on Security Audits
Detailed Analyses of Real-World Security Audits
Case studies provide valuable insights into real-world security audits, showcasing the challenges faced, strategies employed, and outcomes achieved. These detailed analyses offer a practical understanding of how security audits are conducted in various industries and organizational contexts. Case studies help auditors and organizations learn from past experiences, apply best practices, and identify opportunities for improvement in their own security measures.
Lessons Learned
Case studies also provide an opportunity to examine lessons learned from security audits. By analyzing successful and unsuccessful audit experiences, organizations can gain valuable insights into best practices, common pitfalls, and effective strategies for addressing identified security risks. Lessons learned from case studies can guide organizations to develop more robust security measures and improve their overall security posture.
Best Practices Illustrated through Case Studies
Case studies highlight best practices observed during security audits and demonstrate their impact on enhancing security measures. These practices include proactive risk assessment, regular auditing, continuous improvement, and collaboration among stakeholders. Through real-world examples, organizations can understand how best practices in security audits translate into tangible benefits, such as increased resilience to cyber threats and improved protection of valuable assets.
In conclusion, security audits play a vital role in today’s digital era to protect organizations’ assets, systems, and sensitive information. By following a systematic approach, involving various stakeholders, and leveraging tools and techniques, security audits help organizations identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance, and improve their overall security posture. While challenges exist, the future of security audits lies in adapting to emerging technologies, addressing evolving threats, and staying updated with regulatory requirements. Through case studies and lessons learned, organizations can continuously learn and enhance their security measures to safeguard against emerging risks.

I gotta say, security audits are like those dentist appointments you dread but still need. Can’t escape ’em!
Oh, come on! Comparing security audits to dentist appointments? That’s a stretch. A security audit is crucial for protecting sensitive information and preventing potential breaches. It’s not something you can just brush off like a dental check-up. Take it seriously!
“Wow, after reading this article, I had no idea there were so many types of security audits! Who knew? 🤯”
Actually, it’s surprising that you didn’t know about different types of security audits. It’s basic knowledge for anyone remotely interested in cybersecurity. Maybe you should educate yourself more before commenting. 🙄
“Who knew security audits could be so exciting? I’d love to hear some real-life horror stories or success stories. Anyone got any to share?”
Oh please, spare me the excitement of security audits. They’re just a necessary evil to keep our data safe. But if you really want to hear some horror stories, check out the countless data breaches and cyber attacks happening every day. That’s the real world we live in.
“Who knew security audits could be so fascinating? 😄 I never thought I’d be geeking out over the different types of safety audits! 🕵️♀️💼”
Wow, I never thought security audits could be so crucial in our digital age! Who knew? 🤔
“Who even needs security audits? I mean, can’t we just trust our gut instincts? 🤷♂️”
“Who needs security audits anyway? I mean, can’t we just rely on luck and hope for the best?”
Are you serious? Luck and hope? That’s the most naive and reckless approach to security I’ve ever heard. It’s like leaving your door wide open and wishing no one will come in. Wake up! Security audits are essential to protect ourselves from real threats.
Wow, who knew security audits could be so fascinating? I’m still trying to wrap my head around all the different types.