In the realm of Cyber Security, one term that frequently arises is HSM, which stands for Hardware Security Module. These specialized devices play a crucial role in protecting sensitive information and cryptographic keys. They act as fortified vaults, enhancing security measures and minimizing potential vulnerabilities. This article aims to shed light on the significance of HSMs in the world of Cyber Security, unraveling their functions and highlighting their contributions to safeguarding digital assets and maintaining privacy. Whether you are a cybersecurity enthusiast or looking to enhance your knowledge in this field, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the pivotal role HSMs play in maintaining a secure digital environment.
Understanding the basics of HSM
What is HSM
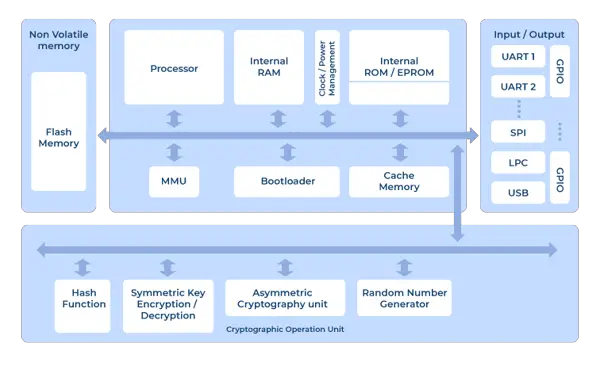
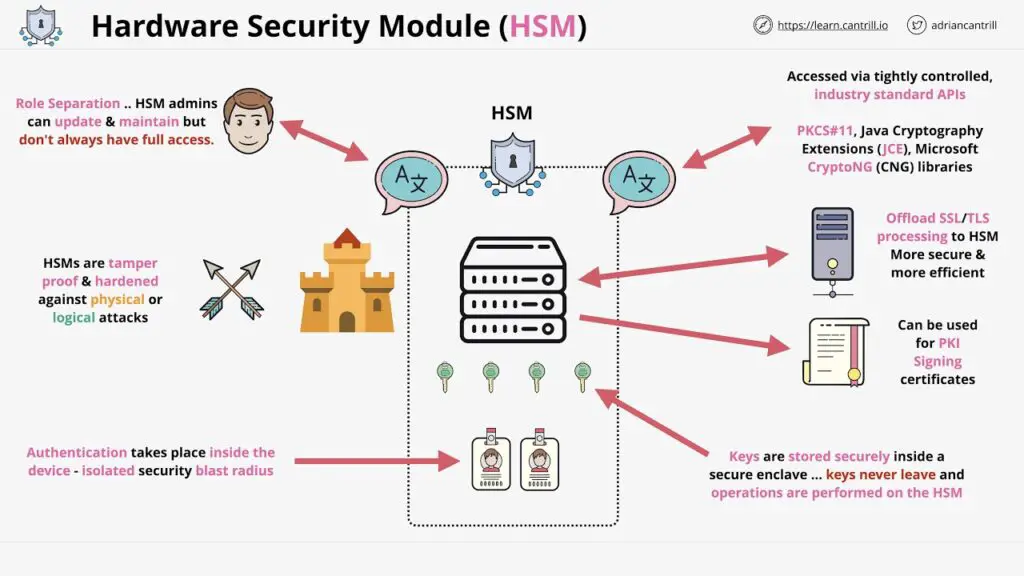
In the world of cybersecurity, HSM stands for Hardware Security Module. It is a specialized device or module that provides secure storage and management of cryptographic keys and performs cryptographic operations. HSMs are designed to be tamper-resistant, making them an essential component in securing sensitive data and ensuring the integrity of cryptographic processes.
Purpose and Functionality of HSM
The primary purpose of an HSM is to safeguard cryptographic keys and ensure they are not vulnerable to theft or unauthorized access. This is crucial because cryptographic keys are the backbone of encryption and security protocols. HSMs provide a secure environment for key generation, storage, and management, protecting them from being compromised.
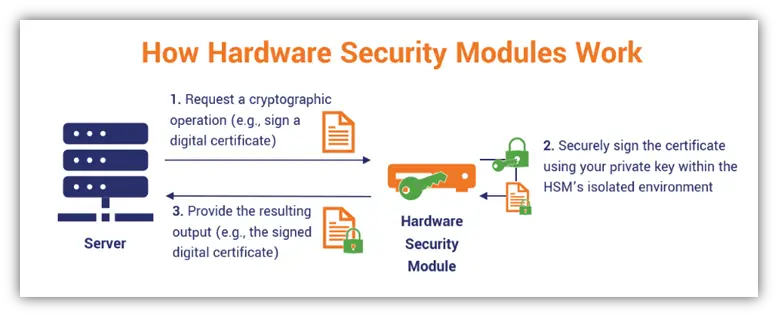
HSMs also offer a range of cryptographic functions, such as encryption and decryption, hashing, and digital signatures. These functions are performed within the secure boundaries of the HSM, preventing any exposure of sensitive data or cryptographic operations to the external environment.
Importance of HSM in Cyber Security
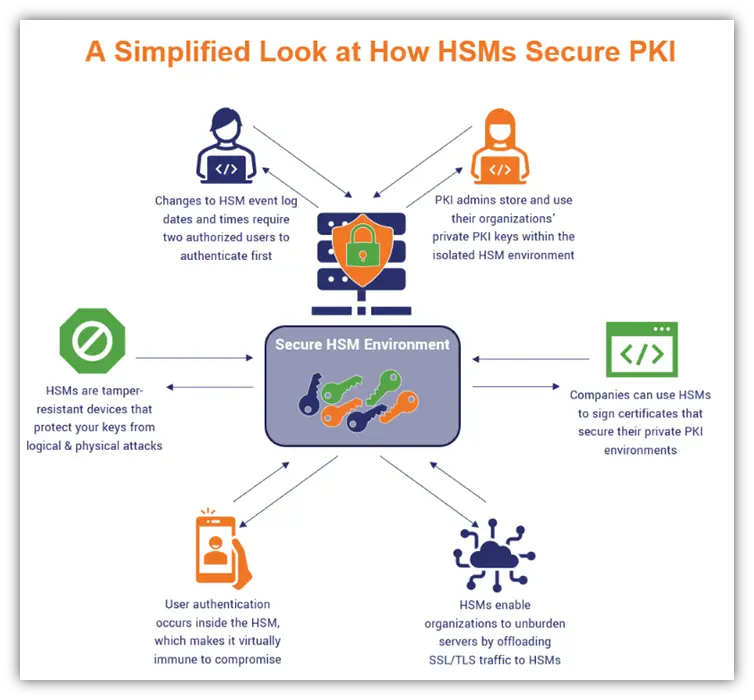
HSMs play a critical role in enhancing cybersecurity. By securely storing cryptographic keys, HSMs prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive data and systems. This is especially important in industries that handle personal and financial information, where data breaches can lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
HSMs also ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital transactions and communications. By generating and managing digital certificates, HSMs enable secure identification, authentication, and non-repudiation. This is vital in today’s interconnected world, where trust and security are paramount for the functioning of various online services, such as e-commerce, online banking, and government applications.
Types of HSM
Hardware-Based HSM
Hardware-based HSMs are physical devices that are dedicated to cryptographic operations and key management. These devices are designed to resist physical attacks, such as tampering and extraction of sensitive information. Hardware-based HSMs provide a high level of security and performance, making them suitable for organizations that require robust protection for their cryptographic assets.
Software-Based HSM
Software-based HSMs, also known as virtual HSMs, leverage the existing computing infrastructure to provide cryptographic services and key management. Instead of a physical device, software-based HSMs are implemented as software libraries or modules that run on servers or cloud environments. While they offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness, software-based HSMs may be more vulnerable to certain types of attacks compared to hardware-based counterparts.
Embedded HSM
Embedded HSMs are integrated within other devices or systems, such as network appliances, IoT devices, or smartphones. They provide secure cryptographic functionality within a specific device or platform, adding an extra layer of security to the overall system. Embedded HSMs are widely used in sectors where security is paramount, such as banking, healthcare, and critical infrastructure.
Comparison of Different Types of HSM
Each type of HSM has its advantages and considerations. Hardware-based HSMs offer the highest level of security and performance, but they may come at a higher cost. Software-based HSMs provide more flexibility and scalability, but their security may be more vulnerable to certain attacks. Embedded HSMs offer localized security within specific devices or systems, but they may have limitations in terms of scalability and integration options. Selecting the right type of HSM depends on the specific needs and requirements of an organization.
Key Components of HSM
Cryptographic Processor
The cryptographic processor is the heart of an HSM. It is responsible for performing cryptographic operations, such as encryption, decryption, and hashing. The processor is designed to execute these operations securely within the boundaries of the HSM, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or leakage.
Secure Key Storage
One of the primary purposes of an HSM is to securely store cryptographic keys. Secure key storage ensures that keys are not vulnerable to theft, tampering, or unauthorized duplication. HSMs employ various techniques, such as hardware encryption and physical protection mechanisms, to safeguard the keys.
Key Lifecycle Management
Key lifecycle management refers to the processes and procedures involved in the generation, distribution, usage, renewal, and termination of cryptographic keys. HSMs provide a secure environment for managing the entire lifecycle of keys, including key generation, key rotation, and key deletion. This ensures that keys are properly managed throughout their lifespan and minimizes the risks associated with key compromise.
Secure Execution Environment
HSMs provide a secure execution environment for cryptographic operations. The environment is isolated from the host system, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring that the integrity of cryptographic processes is maintained. The secure execution environment includes measures, such as secure boot, operating system hardening, and logical access controls, to protect against various types of attacks.
HSM Applications in Cyber Security
Data encryption
One of the primary applications of HSMs in cybersecurity is data encryption. HSMs ensure the secure storage of encryption keys and perform encryption operations securely, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. HSMs are widely used in industries that handle confidential data, such as banking, healthcare, and government agencies.
Database security
HSMs play a crucial role in securing databases. By securely managing encryption keys and performing encryption operations, HSMs protect sensitive data stored in databases from unauthorized access or tampering. HSMs can also enforce access controls and audit trails, enhancing the overall security posture of the database system.
Secure identity and access management
HSMs are essential in secure identity and access management systems. They provide a secure environment for generating and managing digital certificates, ensuring the secure identification and authentication of users. HSMs also support secure storage and distribution of cryptographic credentials, such as smart cards or tokens, which are used for secure access to systems and services.
Digital signatures and certificates
HSMs are widely used for generating and verifying digital signatures, as well as managing digital certificates. Digital signatures provide integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation to digital transactions and documents. HSMs ensure the secure generation and storage of private signing keys, preventing their unauthorized use or theft. They also provide secure verification of digital signatures, establishing trust in the authenticity of digital documents and transactions.
Standards and Certifications in HSM
FIPS 140-2
FIPS 140-2 (Federal Information Processing Standard Publication 140-2) is a U.S. government standard that defines the security requirements for cryptographic modules, including HSMs. HSMs that are compliant with FIPS 140-2 undergo rigorous testing and validation to ensure they meet the specified security criteria.
Common Criteria
Common Criteria is an international standard for evaluating and certifying the security of information technology products. HSMs that are evaluated and certified under the Common Criteria provide assurance that they meet specific security requirements and have undergone independent testing and evaluation.
PCI HSM
PCI HSM is a standard developed by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council for securing cryptographic keys used in payment card processing. HSMs that comply with the PCI HSM standard provide assurance that they meet the security requirements for protecting sensitive payment card data.
Understanding Importance of HSM Certification
Certifications such as FIPS 140-2, Common Criteria, and PCI HSM are important in ensuring the trustworthiness and reliability of HSMs. These certifications provide independent validation of the security features and capabilities of HSMs, giving organizations confidence in their suitability for securing sensitive data and cryptographic operations.
HSM Integration in Cyber Security Architecture
How to Integrate HSM into Existing Infrastructure
Integrating HSMs into an existing cybersecurity architecture requires careful planning and consideration. The integration process involves identifying the key systems and applications that require HSM protection, determining the appropriate type of HSM, and establishing secure communication channels between the HSMs and the systems.
Integration typically involves configuring the systems to utilize the cryptographic services provided by the HSMs, such as encryption and key management. Application programming interfaces (APIs) and cryptographic libraries provided by HSM vendors facilitate the integration process and enable developers to leverage the functionality of the HSMs within their applications.
Challenges of HSM Integration
Integrating HSMs into existing infrastructure may present certain challenges. Some of the challenges include compatibility issues with legacy systems and applications, the need for additional expertise in managing HSMs, and the potential disruption to existing workflows during the integration process.
Potential Solutions for HSM Integration
To address these challenges, organizations can employ various strategies. These include conducting thorough compatibility assessments prior to integration, providing training and support for HSM administration and usage, and implementing a phased integration approach to minimize disruptions. Working closely with experienced HSM vendors and consultants can also help organizations overcome integration challenges.
Case Studies of HSM in Cyber Security
HSM in Banking
HSMs play a critical role in securing banking transactions and protecting customer data. Banks use HSMs to securely manage encryption keys, perform cryptographic operations for secure communication and transaction processing, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. HSMs enable secure online banking, ATM transactions, and interbank communication, safeguarding against fraud and unauthorized access.
HSM in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, protecting sensitive patient data is of utmost importance. HSMs are used to secure electronic medical records, ensure the privacy and integrity of patient information, and comply with healthcare data protection regulations. HSMs also support the secure exchange of medical information between healthcare providers, enhancing collaboration while maintaining data confidentiality.
HSM in Government Agencies
Government agencies handle vast amounts of sensitive data and need to ensure its confidentiality and integrity. HSMs are extensively utilized by government agencies to protect classified information, secure communication channels, and authenticate digital signatures on official documents. HSMs enable secure government-to-government communication, e-passport issuance, and secure online services for citizens.
HSM in E-Commerce
E-commerce platforms rely on HSMs to secure transactions and protect customer payment data. HSMs safeguard the encryption keys used for secure communication between customers and online merchants, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of credit card information. HSMs also enable the secure storage and processing of customer credentials, ensuring a trusted and safe online shopping experience.
The Future of HSM in Cyber Security
Emerging Trends in HSM
The field of HSM is continually evolving to meet the demands of emerging technologies and threats. Some of the emerging trends in HSM include the adoption of cloud-based HSMs, the integration of HSMs with containerized environments, and the integration of HSMs with blockchain technologies. These trends aim to provide enhanced scalability, flexibility, and security in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Impact of Quantum Computing on HSM
The advancement of quantum computing poses a significant challenge to traditional cryptographic algorithms. HSMs will play a crucial role in securing cryptographic keys against quantum attacks by implementing quantum-resistant algorithms, secure key distribution mechanisms, and post-quantum cryptography techniques. The integration of quantum-resistant HSMs into cybersecurity architectures will be essential to mitigate the risks posed by quantum computing.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in HSM
AI and machine learning can be leveraged in HSMs to enhance their security capabilities. These technologies can enable advanced anomaly detection, threat intelligence, and behavior analysis for HSM systems. AI and machine learning algorithms can also assist in predicting and mitigating potential attacks on HSMs, improving overall cybersecurity defenses.

HSM Vendors and Solutions
Major Players in the HSM Market
There are several major players in the HSM market, offering a wide range of HSM solutions to meet various cybersecurity needs. Some of the prominent HSM vendors include Thales, Gemalto (now part of Thales), Utimaco, IBM, and Entrust. These vendors provide hardware-based and software-based HSMs, catering to the diverse requirements of organizations across different industries.
Comparison of Different HSM Solutions
When choosing an HSM solution, organizations should consider factors such as security features, performance, scalability, integration options, and vendor support. It is essential to evaluate the specific needs and requirements of the organization and conduct a thorough comparison of different HSM solutions to make an informed decision.
How to Choose the Right HSM Vendor
Selecting the right HSM vendor requires careful consideration. Organizations should assess factors such as vendor reputation, experience in the field, compliance with industry standards, and the availability of post-sales support and services. It is advisable to consult with cybersecurity experts and seek recommendations from trusted sources before finalizing a decision.
Limitations and Challenges in HSM
Key Vulnerabilities in HSM
While HSMs are designed to be secure, they are not immune to vulnerabilities. Some vulnerabilities in HSMs may arise from design flaws, implementation errors, or attacks targeting underlying systems. It is crucial for organizations to stay informed about potential vulnerabilities and promptly apply patches and updates provided by HSM vendors to mitigate these risks.
Critiques and Controversies of HSM
Like any technology, HSMs have faced critiques and controversies. Some of the criticisms include concerns over the complexity and cost of implementing HSMs, the potential over-reliance on a single point of failure, and the challenges associated with interoperability and integration with legacy systems. Addressing these concerns requires a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s specific requirements and careful planning and implementation.
Overcoming HSM Challenges and Limitations
To overcome the challenges and limitations of HSMs, organizations can implement best practices and adopt a layered approach to cybersecurity. This includes regular audits and assessments of HSM systems, continuous employee training and awareness programs, and the implementation of multi-factor authentication and access controls. Regularly reviewing and updating security policies and leveraging the expertise of cybersecurity professionals can also contribute to mitigating HSM-related challenges.
In conclusion, HSMs play a vital role in enhancing cybersecurity by providing secure storage and management of cryptographic keys and ensuring the integrity of cryptographic operations. Different types of HSMs offer varying levels of security and functionality, allowing organizations to choose the most suitable option based on their specific needs. Integration of HSMs into existing cybersecurity architecture requires careful planning and consideration, but it provides numerous benefits, including data encryption, database security, and secure identity and access management. HSMs are certified according to various standards to ensure their trustworthiness and reliability. The future of HSM lies in emerging trends such as cloud-based HSMs, integration with emerging technologies like quantum computing and AI, and the continuous development of secure and scalable solutions. As organizations navigate the complex landscape of HSM vendors and solutions, it is essential to consider factors such as security features, performance, scalability, and vendor support. While HSMs have their limitations and face certain vulnerabilities, these challenges can be overcome through best practices, continuous monitoring, and staying informed about potential risks. By understanding the basics of HSMs and their applications in cybersecurity, organizations can strengthen their defensive capabilities and protect their sensitive data from malicious actors.