In the world of cybersecurity, one of the fundamental techniques used to identify and track potential threats is called fingerprinting. Fingerprinting is the process of gathering unique characteristics and attributes from a computer or network in order to distinguish it from others. By understanding fingerprinting techniques, experts can effectively analyze and detect suspicious activities, ultimately enhancing the overall security of digital systems. In this article, we will delve into the concept of fingerprinting and explore its importance in maintaining a secure online environment. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries behind fingerprinting techniques in cyber security!
Fingerprinting in Cyber Security Defined
Understanding the Concept of Fingerprinting
In the realm of cyber security, fingerprinting refers to the process of identifying and gathering specific information about a system or network to create a unique profile or “fingerprint.” This fingerprint can then be used to identify and categorize different devices, applications, or users based on their specific characteristics and behaviors. Fingerprinting plays a crucial role in cyber security as it helps in detecting threats, securing networks, and implementing targeted security measures.
The Importance of Fingerprinting in Cyber Security
Fingerprinting techniques are essential in cyber security for several reasons. Firstly, they enable the identification of different devices or systems connected to a network, enabling network administrators to monitor and manage them effectively. Secondly, fingerprinting helps in detecting and analyzing cyber threats and attacks by identifying their unique characteristics and patterns. This allows organizations to proactively defend their systems and networks against potential intrusions or vulnerabilities. Lastly, fingerprinting can be used for user authentication and access control, ensuring that only authorized individuals can gain entry to sensitive data or resources.
Types of Fingerprinting in Cyber Security
Active Fingerprinting
Active fingerprinting involves actively probing a target system or network to gather specific information and analyze its unique characteristics. It typically involves sending test packets or generating specific traffic patterns to elicit a response from the target. By analyzing the responses, active fingerprinting can determine the operating system, applications, and even version numbers running on the target system. However, this method can be more intrusive and may trigger security alerts or raise suspicions.
Passive Fingerprinting
Unlike active fingerprinting, passive fingerprinting does not involve any direct interaction with the target system. Instead, it relies on monitoring and analyzing network traffic and collecting information based on observed behaviors, patterns, or characteristics. Passive fingerprinting is less intrusive and can provide valuable insights into the composition and behavior of a network without alerting the target system. It is particularly useful when conducting network reconnaissance or gathering intelligence about potential threats.
Hybrid Fingerprinting
As the name suggests, hybrid fingerprinting combines elements of both active and passive techniques to create a more comprehensive fingerprint. By using a combination of active probing and passive monitoring, hybrid fingerprinting aims to gather a wider range of information about a target system or network. This approach leverages the benefits of both techniques while mitigating their drawbacks. Hybrid fingerprinting provides a more detailed and accurate profile, making it a valuable tool for cyber security professionals.

Active Fingerprinting Explained
The Process of Active Fingerprinting
Active fingerprinting typically involves sending specially crafted packets or requests to a target system or network and analyzing the responses. These requests are designed to exploit certain characteristics or vulnerabilities unique to specific operating systems or applications. The responses received can then reveal valuable information about the target, including its operating system, open ports, protocols in use, or even installed applications and services. Active fingerprinting techniques include protocols like ICMP, TCP SYN, and UDP probes.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Active Fingerprinting
Active fingerprinting offers several benefits, including the ability to gather highly accurate and detailed information about a target system or network. This information can help in understanding potential vulnerabilities, assessing security risks, and implementing appropriate security measures. However, there are also some drawbacks to active fingerprinting. It can be more intrusive and may trigger security alerts or defensive responses from the target. Additionally, it requires active interaction with the target, which may not always be feasible or desirable.
Understanding Passive Fingerprinting
How Passive Fingerprinting Works
Passive fingerprinting involves observing and analyzing network traffic without actively interacting with the target system or network. By monitoring characteristics such as packet headers, payload behavior, or timing information, passive fingerprinting can extract valuable information about the devices, applications, or protocols in use. This information can help in identifying the operating system, software versions, or even the behavior of specific network users. Passive fingerprinting techniques include analyzing network traffic using tools like Wireshark or analyzing log files.
Advantages and Limitations of Passive Fingerprinting
Passive fingerprinting offers several advantages in terms of its non-intrusive nature and the ability to gather information without alerting the target. It is especially useful when conducting network reconnaissance or monitoring network behavior over extended periods. However, passive fingerprinting has its limitations. It may not provide as detailed or accurate information as active fingerprinting since it relies solely on observed behaviors. Additionally, some techniques may be subject to noise or interference, impacting the reliability of the gathered information.

Hybrid Fingerprinting: A Combination Approach
Process of Hybrid Fingerprinting
Hybrid fingerprinting combines active and passive techniques to gather a wider range of information about a target system or network. The process generally involves using active techniques to gather specific information, such as operating system characteristics, and then supplementing it with passive techniques to capture additional behavior patterns. This combined approach aims to overcome the limitations of each technique individually and provide a more comprehensive fingerprint. Hybrid fingerprinting can provide a more accurate profile, covering both static and dynamic information.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Hybrid Fingerprinting
The strengths of hybrid fingerprinting lie in its ability to collect both active and passive data, offering more precise information about a target system or network. By combining the benefits of each technique, hybrid fingerprinting can provide a more accurate and detailed profile, improving the effectiveness of cyber security measures. However, this approach may require more resources and time compared to individual techniques. Additionally, it may still trigger some security systems, depending on the level of interaction involved in the active component.
Fingerprinting Techniques in Detail
TCP/IP Fingerprinting
TCP/IP fingerprinting involves analyzing the characteristics of TCP/IP packets to identify the specific operating system or network stack being used. By examining various packet attributes, such as TCP initial sequence numbers, window sizes, or TTL values, unique patterns can be identified that are associated with specific operating systems. TCP/IP fingerprinting is commonly used for network mapping, intrusion detection, and vulnerability assessment.
HTTP Fingerprinting
HTTP fingerprinting focuses on analyzing the characteristics of HTTP traffic to identify specific web servers, applications, or content management systems being used. It involves examining HTTP headers, response codes, or server-specific behaviors to create a unique fingerprint. HTTP fingerprinting can be useful for web application security, identifying vulnerable systems, or detecting potentially malicious activity.
Device Fingerprinting
Device fingerprinting aims to identify and categorize specific devices based on their unique characteristics and behaviors. This can include attributes such as device MAC addresses, hardware configurations, or even the relationships between multiple devices. Device fingerprinting can enable more granular access control and user authentication, ensuring that only authorized devices can connect to a network or access specific resources.
Browser Fingerprinting
Browser fingerprinting focuses on identifying and tracking individual users based on the unique characteristics of their web browsers and devices. This can include attributes such as user agent strings, installed plugins or extensions, screen resolutions, or even fonts installed on the device. Browser fingerprinting is often used for targeted advertising, user profiling, or fraud detection.

Roles of Fingerprinting in Cyber Security
Detecting Cyber Threats
Fingerprinting plays a crucial role in detecting and analyzing cyber threats by identifying their unique characteristics or patterns. By comparing the fingerprints of known threats with the characteristics observed in network traffic or device behavior, potential threats can be detected and mitigated. Fingerprinting techniques can help in identifying malware, intrusion attempts, or unauthorized access attempts, enabling organizations to take appropriate measures to protect their systems and networks.
Network Security
Fingerprinting techniques are essential for network security as they enable the identification and monitoring of devices connected to a network. By creating fingerprints for each device, network administrators can detect unauthorized devices or anomalous behavior and take appropriate action. Fingerprinting can also help in identifying vulnerable or outdated software versions, allowing organizations to patch or update systems in a timely manner to avoid potential security risks.
Web Application Security
In the realm of web application security, fingerprinting techniques are crucial for identifying and assessing potential vulnerabilities. By analyzing HTTP traffic or examining web application components, fingerprinting can reveal weaknesses or misconfigurations in web applications that can be exploited by attackers. This information can then be used to implement appropriate security measures or patches to safeguard against potential attacks.
Anti-spam and Anti-fraud Measures
Fingerprinting plays a role in combating spam and fraud by identifying patterns or characteristics associated with malicious activity. For example, browser or device fingerprinting can be used to detect and block malicious bots or prevent fraudulent transactions. By utilizing fingerprinting techniques, organizations can enhance their anti-spam and anti-fraud measures, reducing the impact of these threats and protecting their users or customers.
Challenges and Limitations of Fingerprinting Techniques
False Positives and False Negatives
One of the primary challenges of fingerprinting techniques is the potential for false positives or false negatives. False positives occur when a system or network is wrongly classified, leading to unnecessary security measures or alerts. On the other hand, false negatives occur when a threat or vulnerability goes undetected due to an inaccurate or incomplete fingerprint. Striking a balance between minimizing false positives and false negatives is a constant challenge in fingerprinting for cyber security.
Handling Encrypted Traffic
The increasing use of encryption protocols, such as HTTPS or VPNs, poses challenges for fingerprinting techniques that rely on analyzing network traffic. While the encryption ensures data confidentiality, it also makes it difficult to extract valuable information from the encrypted packets. This means that fingerprinting techniques need to adapt and find innovative ways to handle encrypted traffic while still maintaining privacy and security.
Adapting to Changing Cyber Threat Landscape
Cyber threats and attack techniques are continually evolving, making it challenging for fingerprinting techniques to keep up. Attackers may employ sophisticated evasion techniques or mask their activities, making it harder to detect or profile them accurately. Fingerprinting techniques need to continuously evolve, adapt, and incorporate new methods or technologies to stay effective in the face of a rapidly changing cyber threat landscape.
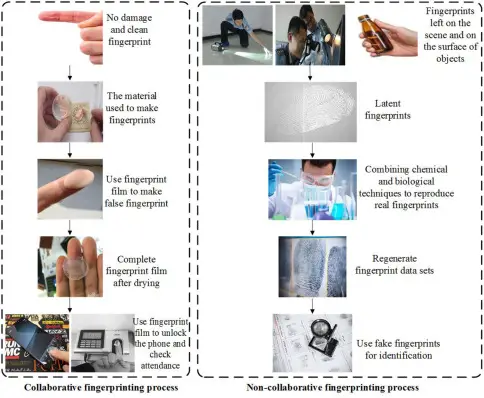
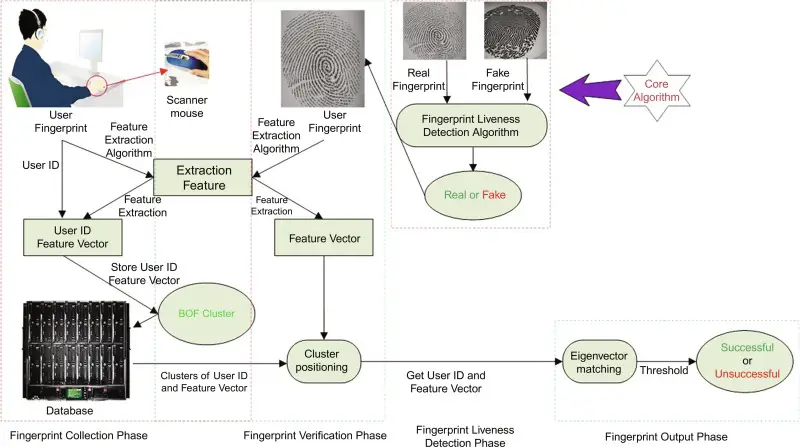
Improving Fingerprinting Techniques in Cyber Security
Innovative Approaches for more Accurate Fingerprinting
To enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of fingerprinting techniques, researchers and analysts continually explore innovative approaches. This includes methods such as machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that can analyze vast amounts of data and patterns to identify unique characteristics or behavior patterns. Additionally, advances in data mining, statistical analysis, and pattern recognition can contribute to more accurate and reliable fingerprinting techniques.
Integration with Other Cyber Security Measures
Fingerprinting techniques can be further improved by integrating them with other cyber security measures and technologies. Collaboration with intrusion detection systems (IDS), firewalls, or security information and event management (SIEM) systems can enhance the overall threat detection capabilities by correlating fingerprints with other security alerts and indicators. By combining various sources of data and intelligence, organizations can strengthen their overall security posture.
Leveraging Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning and AI can play a significant role in the advancement of fingerprinting techniques. By training algorithms on large datasets, these technologies can improve the accuracy and efficiency of fingerprinting, enabling more precise identification and classification of devices, applications, or threats. Additionally, machine learning can assist in adapting fingerprinting techniques to changing threat landscapes and automating the process to handle high volumes of data.
Future Trends in Fingerprinting for Cyber Security
Impact of Emerging Technologies
The future of fingerprinting in cyber security is likely to be influenced by emerging technologies. The growing adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing presents new challenges and opportunities for fingerprinting techniques. The increasing interconnectedness of devices and systems and the vast amount of data generated create a need for more advanced fingerprinting methods to manage and secure these environments effectively.
Evolving Cyber Threats and Countermeasures
As cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, fingerprinting techniques will need to evolve as well. Attackers may employ advanced evasion techniques or leverage new technologies, such as artificial intelligence or machine learning, to bypass traditional fingerprinting methods. Consequently, fingerprinting techniques will need to enhance their capabilities, integrate with advanced defense mechanisms, and continually adapt to emerging threats.
Legal and Ethical Considerations of Fingerprinting Techniques
The use of fingerprinting techniques in cyber security raises legal and ethical considerations. The collection and analysis of personal data, such as device or browser fingerprints, may raise privacy concerns and require compliance with relevant regulations. Organizations must ensure that their fingerprinting practices adhere to applicable laws and regulations, while also respecting user privacy and providing transparency in how their data is used and protected.
In conclusion, fingerprinting techniques play a vital role in cyber security by enabling the identification, categorization, and analysis of devices, applications, or network behavior. Active, passive, and hybrid fingerprinting approaches each have their strengths and limitations. TCP/IP fingerprinting, HTTP fingerprinting, device fingerprinting, and browser fingerprinting are commonly used techniques. Fingerprinting contributes to detecting cyber threats, enhancing network security, securing web applications, and implementing anti-spam and anti-fraud measures. However, fingerprinting techniques face challenges such as false positives or negatives, handling encrypted traffic, and keeping up with evolving cyber threats. To improve fingerprinting techniques, innovative approaches, integration with other security measures, and utilization of machine learning and AI can be leveraged. Looking ahead, the future of fingerprinting in cyber security will be shaped by emerging technologies, evolving cyber threats, and the need for legal and ethical considerations in data collection and usage.
“Who knew fingerprints could be so important in cyber security? Mind blown!”
Seriously? It’s not exactly rocket science. Fingerprints have been used for identification purposes for ages. It’s about time they got integrated into cyber security. Don’t act so surprised, buddy.
“Who knew fingerprints were so important in cyber security? Mind-blown!”
Seriously? You’re just figuring that out now? It’s been common knowledge for years. Catch up, mate.
Wow, fingerprinting in cyber security is like CSI for hackers! Who knew? 🕵️♂️🔍🔒 #MindBlown
“Who knew fingerprints could be so useful in catching cyber criminals? Technology never ceases to amaze me!”
Well, it’s about time you caught up with the rest of us. Fingerprint technology has been used for years in crime investigation. Maybe next time, try to keep up with the times before making such ignorant comments.
“Who needs fingerprinting in cyber security when we have unicorns and rainbows to protect our data? 🌈🦄”
“Who needs fingerprinting when you can just change your digital identity like a chameleon? 🦎🧐”
Wow, fingerprinting in cyber security is fascinating! Who knew our fingerprints could be so useful online?
Actually, fingerprints in cyber security aren’t all that unique or foolproof. They can be easily faked or bypassed. It’s just another gimmick to give us a false sense of security. Don’t believe the hype.